Unit 1-5 Vocab
Unit 1
- int, boolean, char, and double are primitives
- Strings and other classes are objects
- Compare primitives with == and objects with .equals()
- Objects have properties while primitives do not
- casting is when you assign a value of one primitive data type to another type. In integer division, the decimal is truncated. You need to use a double in order to keep the decimal
- casting rounds down while Math.round rounds to the nearest int
int a = 7;
int b = 3;
System.out.println(a/b);
System.out.println((double)a/(double)b);
Unit 2
- Objects are instances
- Methods have to specify return type which can be void, or nothing
- Static methods tied with the class and defined once across all instances
- Method overloading is when multiple methods with the same name have different parameters
- Wrapper classes allow you to use primatives as objects. One use case would be in arraylists, where only objects are stored. Ex: ArrayList
myNumbers = new ArrayList (); </li> </ul> </div> </div> </div> @Type(type="json") @Column(columnDefinition = "jsonb") private Map<String,Map<String, Object>> stats = new HashMap<>(); public Integer height; public Integer weight; // Constructor used when building object from an API public Person(Integer weight, Date dob) { this.height = height; this.weight = weight; }
- Concatanation is when you combine primatives together. For example, you would use the .append for combining two strings. You could use "+" to add together integers and doubles. You can concatanate a string with an integer through "+".
String a = "test "; String b = "this"; System.out.println(a+b);
- Math.round rounds to the nearest int
- Math.random gives a random number between two numbers
double a = 3.54; double b = 3.49; System.out.println(Math.round(a)); System.out.println(Math.round(b));
boolean t = true; boolean f = false; if (t) { System.out.println("1"); } if (f) { System.out.println("2"); } if (f && !t) { System.out.println("3"); } if (t && !f) { System.out.println("4"); } if (t || f) { System.out.println("5"); } if (!t || !f) { System.out.println("6"); } if ((t && !f) && (t || f)) { System.out.println("7"); } if ((!t || (t && f)) || t ) { System.out.println("8"); } if (!((f || !t) || (f && t))) { System.out.println("9"); } if (!((f && !t) || (f || t))) { System.out.println("10"); }
- Truth Tables used to see the values of boolean expressions
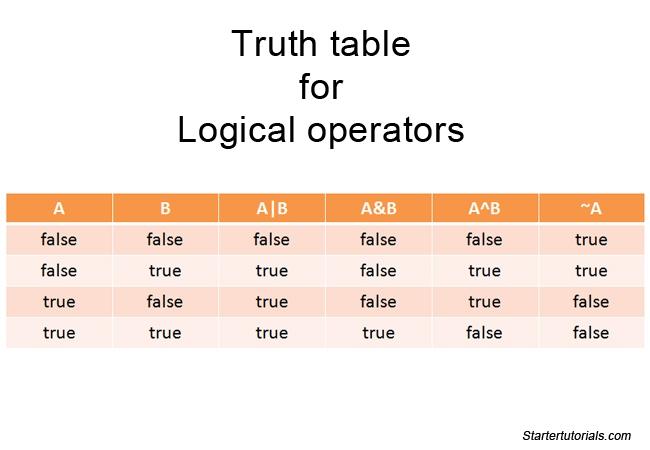
- De Morgan's Law is in essence, Not (A and B) is the same as Not A or Not B
- Remember that "!" denotes Not.
boolean test1 = true; boolean test2 = true; if (!(test1 && test2)){ System.out.println("Test1 and Test2 are both false"); } else{ System.out.println("They are both true"); }
boolean test1 = true; boolean test2 = true; if (!test1 || !test2){ System.out.println("Test1 and Test2 are both false"); } else{ System.out.println("They are both true once again"); }
- While loops run when conditional is true
- Do While loop runs once no matter what and then checks conditionals
int i=1; do{ System.out.println(i); i++; }while(i<=10);
int i=11; do{ System.out.println(i); i++; }while(i<=10);
- nested loops are loops used inside each other
- this can be seen in our monkey nursery rhyme thing
- Classes are created using the class keyword and the first letter is capitalized
- main method class is the tester. Automatically called
public class Person { // automatic unique identifier for Person record @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private Long id; // email, password, roles are key attributes to login and authentication @NotEmpty @Size(min=5) @Column(unique=true) @Email private String email; @NotEmpty private String password; // @NonNull, etc placed in params of constructor: "@NonNull @Size(min = 2, max = 30, message = "Name (2 to 30 chars)") String name" @NonNull @Size(min = 2, max = 30, message = "Name (2 to 30 chars)") private String name; @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") private Date dob; // inches public Integer height; public Integer weight; /* HashMap is used to store JSON for daily "stats" "stats": { "2022-11-13": { "calories": 2200, "steps": 8000 } } */ @Type(type="json") @Column(columnDefinition = "jsonb") private Map<String,Map<String, Object>> stats = new HashMap<>(); // Constructor used when building object from an API public Person(String email, String password, String name, Integer height, Integer weight, Date dob) { this.email = email; this.password = password; this.name = name; this.dob = dob; this.height = height; this.weight = weight; } // A custom getter to return age from dob attribute public int getAge() { if (this.dob != null) { LocalDate birthDay = this.dob.toInstant().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toLocalDate(); return Period.between(birthDay, LocalDate.now()).getYears(); } return -1; } // note this is just an example. just doing bmi *10 public int numberofsteps() { int numberofsteps = (int) (weight/Math.pow(height, 2) *703 *10); return numberofsteps; } public String toString() { return ( "{ \"email\": " +this.email+ ", " + "\"password\": " +this.password+ "\"name\": " +this.name+ "\"height\": " +this.height+ "\"weight\": " +this.weight+ "\"dob\": " +this.dob+ " }" ); } public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException { Date dob = new SimpleDateFormat("MM-dd-yyyy").parse("01-28-2006"); //no arg Person test = new Person(); System.out.println(test); //arg Person test2 = new Person("wutwilliam@gmail.com", "CyberPatriot1!", "William Wu", 71, 180, dob); System.out.println(test2); System.out.println(test2.numberofsteps()); System.out.println(test2.toString()); } }
- getters and setters can both be seen in use in this code
- they get and set properties of an object
- this keywords gets access to properties of the class
- public = accessible anywhere
- private = accessible only in its own class
- static methods dont need an object. part of the class. only initialized once at the start of the execution
public class Example { public static void ex() { System.out.println("no object needed"); } public static void main(String[] args){ ex(); } } Example.main(null);
- extends in when a class is inherited from a different class
- subclass = class that inherits
- superclass = class inherited from
public class Super { public void ex() { System.out.println("test output"); } }
public class Sub extends Super { public static void main (String[] args) { Sub ex1 = new Sub(); ex1.ex(); } } Sub.main(null);
</div>- toString() returns value to string. automatically ran. can be overrided
-
hashCode() returns the hash code of an object
-
Polymorphism is when you have multiple methjods with the same name but different parameters.
- Overloading is when you have multiple methods with the same name but different parameters.
- Overriding is when you have a method with the same name and parameters as a method in a superclass but you want to modify the method in the subclass.
- Late binding is when you have allow the compiler to determine which method to use at runtime instead of compile time.
- Big O notation tells you the number of operations an algorithm will make. Determines efficiancy